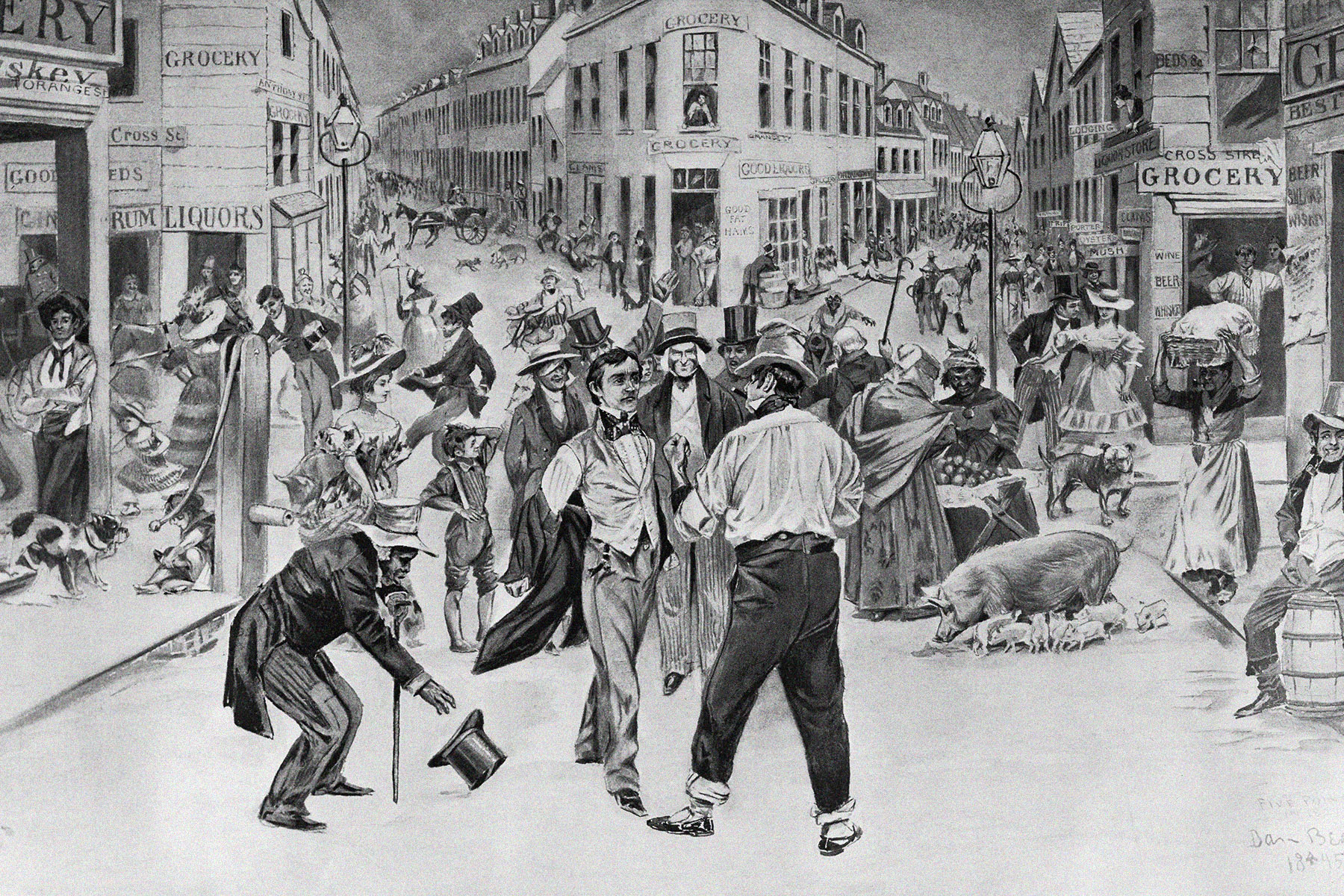
We Asked an Anthropologist About the Gangs of 19th-Century New York
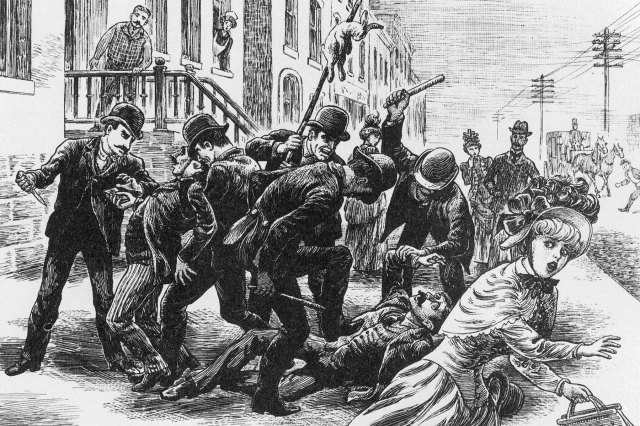
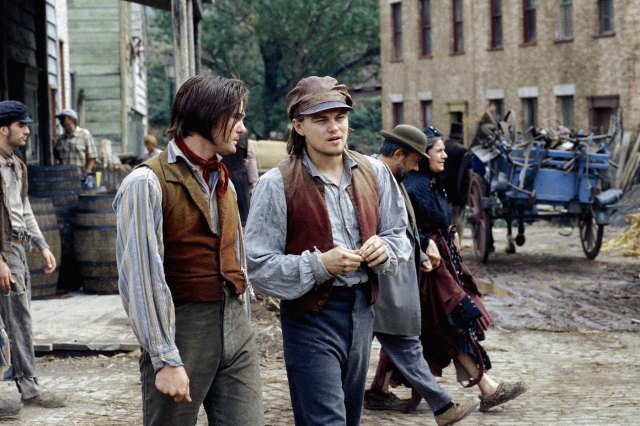
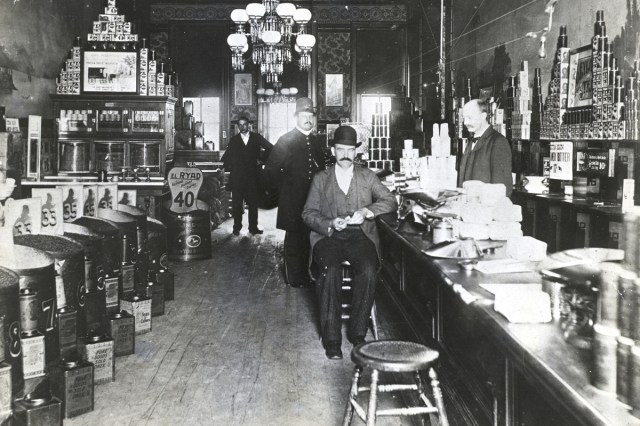
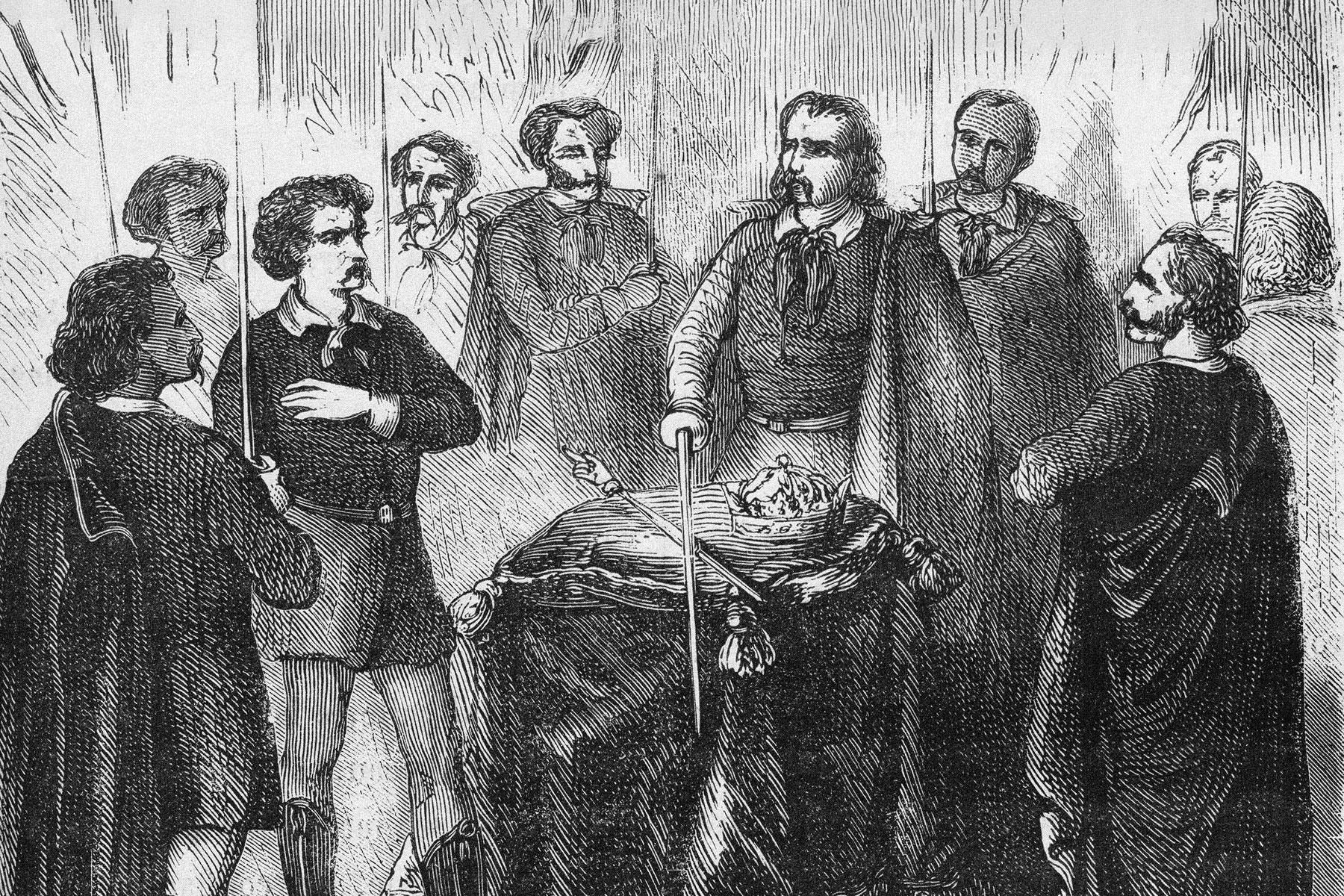
Beginning in the 1830s, a combination of poverty, rapid industrialization, and immigration contributed to the rise of notorious street gangs throughout New York City. For the next several decades, these groups ran rampant until being largely replaced by organized crime syndicates toward the end of the 19th century. But during their heyday, gangs such as the Bowery Boys and Dead Rabbits ruled the streets of New York, particularly a neighborhood in southern Manhattan known as the Five Points. This turbulent period in New York City was marked by violence and corruption, events that were brought to the silver screen in Martin Scorsese’s 2002 historical drama Gangs of New York.
While that film is based on realities of the time, it also furthered several misconceptions about this crime-ridden era. We reached out to anthropologist R. Brian Ferguson, a professor at Rutgers University-Newark and author of the 2023 book Chimpanzees, War, and History, to learn more about this volatile period in NYC history. Ferguson has spent decades studying and teaching how conflict permeates throughout society, and was interviewed for the 2002 documentary Uncovering the Real Gangs of New York, a special feature included on DVD copies of the Scorsese film.
(Editor’s note: This interview has been edited for length and clarity.)
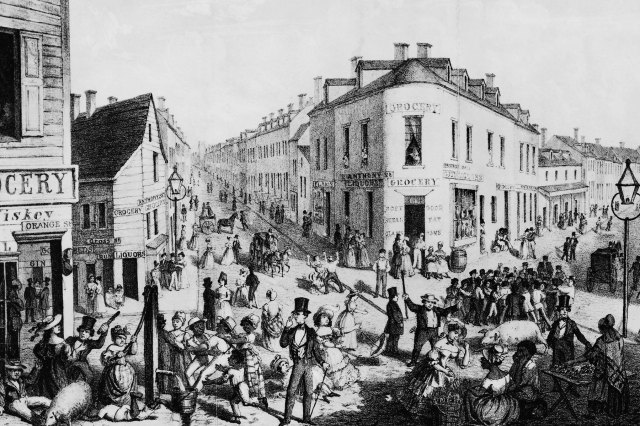
HISTORY FACTS: What was life like in New York City’s Five Points neighborhood?
FERGUSON: Well, the Five Points was from the intersection of different streets, and it began as a residential neighborhood but it was built on landfill from filling in a big lake. So it was wet, and it was sinking, which meant that it was full of diseases in the summer. By 1827, it was already disreputable. Mainly poor people who had no choice about where to live were there — it was the bottom for New York society.
For decades it became — not just in New York, but internationally — famous for incredible squalor and crime and drunkenness and prostitution. It became a symbol for all of that. It was also a highly political environment, and the politics of the time were more contentious in New York than what we’re seeing today in our own lives. It was really a tough time politically.
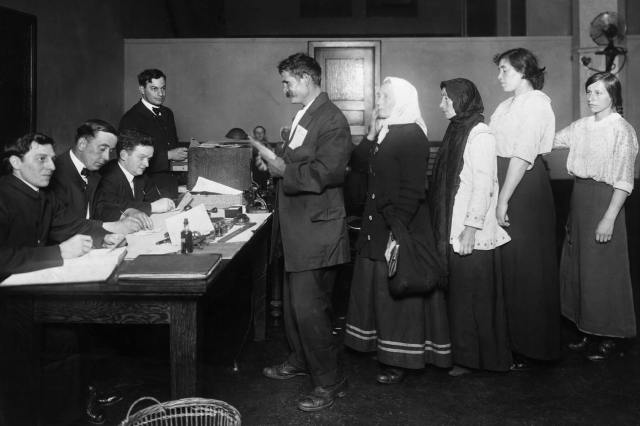
HISTORY FACTS: Speaking of politics, I know Tammany Hall was a big player in New York City. What was Tammany Hall and how did it play a role in local politics?
FERGUSON: Tammany Hall was the Democratic political machine. It won elections, gave out patronage; it was famous for corruption and vote fraud. But besides that, it was the only kind of government that did anything for the poorest of the poor. In the 1840s, it had found its base in immigrants who were pouring into New York, many of whom were Catholic, which Protestant America generally hated.
Tammany Hall was controlled by political ward politicians from the street up, using force. It wasn’t a top-down organization as it once was, but it was really responding to what was happening on the streets, like in the Five Points. The Five Points was its central power base because it was so densely populated. It was known as the “Bloody Ould Sixth Ward,” and the votes from there could control mayors, city government, even tip state and presidential elections.
Love it?75